Atoms
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-04-08
Topic: 99 see comments
Post views: 1236
The Atom
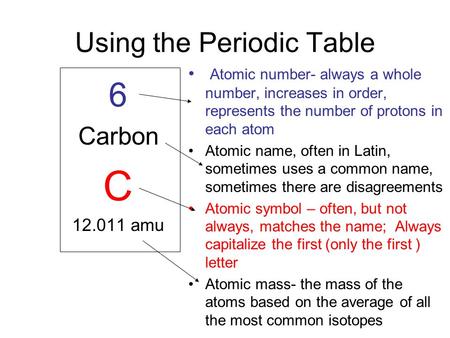
The word ‘atom’ means ‘indivisable’ and an atom is the smallest unit of an element.
Mass Of An Atom:
A proton and neutron have the same mass, equal to one atomic unit of mass (abbreviated to a.m.u). In SI units, one a.m.u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg (to 3 s.f). An electrons mass is much smaller and can be approximated to zero.
Electric Charge Of An Atom:
Neutrons carry no charge and are neutral. Protons are positively charged and electrons carry a negative charge. This is often referred to as the elementary charge and given the symbol ‘e’. To summarise:
- Proton has charge +e
- Electron has charge -e
The SI unit of charge is the coulomb (C).
In SI units, e = 1.602 × 10-19 C (to 4 s.f).
Note - One ampere (A) represents a current flow (I) (flow of charge) of 1 coulomb per second. (6.25 × 1018 electrons per second).
Ions:
There are circumstances including some types of chemical bonding, when an atom may gain or lose, one or more electrons.
- Negative ion: An atom that has gained one or more electrons, has a net negative charge, is known as a negative ion.
- Positive ion: An atom that has lost one or more electrons, has a net positive charge, and is known as a positive ion.
In general, any charged atom is known as an ion.
Notation:
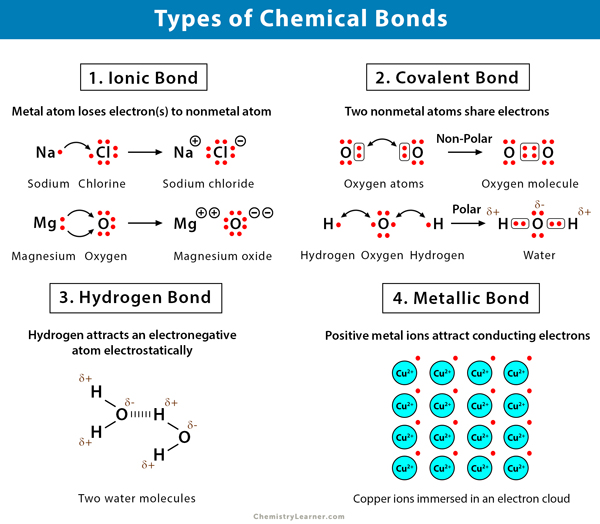
Na+ ⇢ The positive sign shows that the atom (Sodium) has lost an electron and has a positive charge equal to +e.
Mg2+ ⇢ The 2+ sign shows that the atom (Magnesium) has lost two electrons and has a positive charge of +2e.
Cl- ⇢ The - sign shows that this atom (Chlorine) has gained an electron and has a negative charge of -e.
Molecules & Compounds:
Atoms can combine with eachother to form molecules, through the formation of chemical bonds. A molecule may contain two or more of the same type of atom, or it may form a compound containing different types of atoms.
Types Of Chemical Bonding:
- Ionic Bonding - Where one atom ‘donates’ one or more electrons to another atom.
- Covalent Bonding - Where two atoms ‘share’ one or more electrons.
- Metallic Bonding - Where the outer electrons from many metal atoms become seperated from their original nuclei to become ‘free electrons’ that hold the structure together and can move through it.
Isotopes:
Isotopes are forms of the same chemical element (e.g carbon 12, carbon 13) that have the same number of protons in their nucleus but a different number of neutrons, therefore they have a different atomic mass.
Note that isotopes have the same number of protons or else they would be different elements.
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|