(SUVAT) Equations Of Motion
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-06-01
Topic: 117 see comments
Post views: 1245
pinned
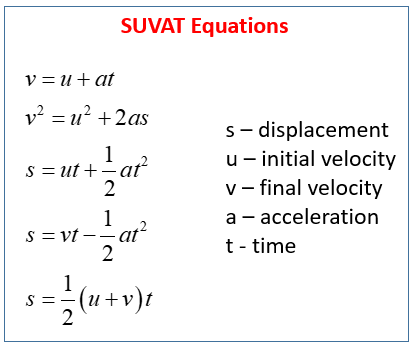
Equations Of Uniform Motion (kinematics)
- v = u0 + at
- x = x0 + u0t + ½at2
- v2 = u02 + 2ax
x/s = Displacement (m)
v0/u0 = Initial velocity (ms-1)
v = Final velocity (ms-1)
a = Acceleration (ms-2)
t = Time (s)
x0 = Initial displacement (m)
For an object moving at a constant velocity where there is no resultant force causing the velocity to change:
s = vt
s = displacement (m)
v = velocity (ms-1)
t = time (s)
For a body starting from rest and moving in a straight line, subject to a constant acceleration:
v = at
and:
s = ½at2
v = velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
In these cases the initial velocity is zero.
For any object starting from an initial velocity u (in ms-1) and subject to a constant acceleration a (in ms-2), the equations of motion are:
v = u0 +at
and:
s = x0 + u0t + ½at2
These equations can be manipulated to give:
s =½(u0 + v)t
v2 = u02 + 2as
s = vt - ½at2
Because displacement, velocity and acceleration are vector quantities, it is important to specify a direction as well as a magnitude for these equations.
The Open University T193 module uses the convention that up is positive and down is negative. This means that acceleration due to gravity would be a negative -9.8 ms2
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|