Forming
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-07-02
Topic: 140 see comments
Post views: 1096
Forming
The forming process involves shaping materials while they are solid, by squeezing, squashing, hammering, bending or stretching the material into the required shape.
Types of forming
Extrusion and wire drawing
Video: https://youtu.be/iiGlq7408ME
For extrusion, raw material is heated and pushed through a shaped hollow die by sliding a piston or a ram. The raw material may be in the form of a cast ingot (billet). The solid material deforms plastically and takes up the shape of the die which can have almost any shape - so if the die is circular, a rod is produced.
It is also possible to produce hollow sections using extrusion.
For using extrusion with polymers, a screw is used similar to injection moulding.
Wire drawing
Wire drawing is a very similar process used to reduce the cross-section of a wire by pulling it through one or more dies with decreasing diameters. It differs from extrusion because the wire is pulled rather than pushed through the die, and unless the wires are quite large, it is usually carried out at room temperature.
Rolling
In rolling, material is passed through the gap between two rotating rollers that squeeze the material as it passes between them.
Sheet steel and aluminium for the bodies of cars and domestic appliances is made this way. Rolled sheet is often termed as a semi-finished product because it requires further processing to shape it into the final product.
Rolling is not restricted to flat sheets, if the desired product has a contoured surface, then by using profiled rollers the contour can be rolled on. An example is corrugated perspex which is sometimes used on roofs to allow light to pass through.
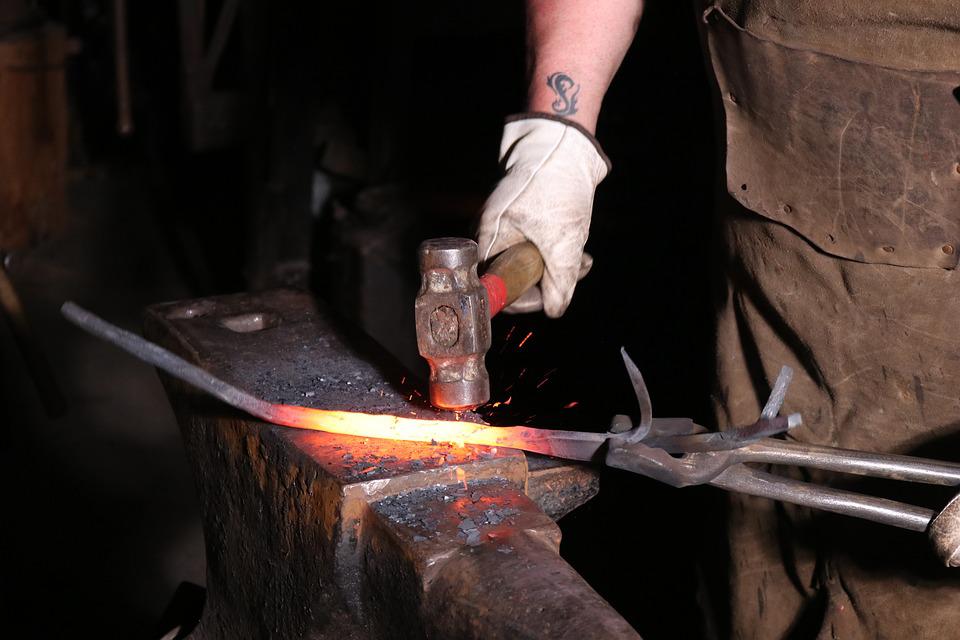
Forging
Video: https://youtu.be/YobXFODkp50
Forging is the process in which a piece of (usually hot) metal is formed into the desired shape by hammering, pressing, rolling etc.
In closed die forging, components are made in one action, being squeezed between upper and lower shaped dies. The force needed to close the dies together depends on both the size of the component and the temperature since the yield stress reduces as the forging temperature increases.
Sheet forming process
Objects made sheet materials such as metal sheets or plastic can be formed in a number of various ways. What all these processes have in common is the form of their starting material - extruded or rolled sheet - and what happens to the material during forming: some combination of bending, stretching and shearing.
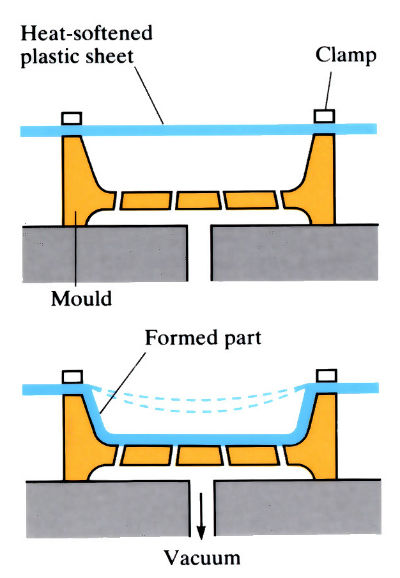
A typical sheet forming process is the forming of shaped panels through pressing (known as press forming), such as those for car bodies, washing machines, filing cabinets, and so on. A vast range of plastics packaging products are also made this way, often by vacuum forming, in which the polymer sheet is heated, stretched onto a single-surface mould and forced against the mould by applying suction.
Powder processing
Powder processing involves filling a mould with powder, which is then compressed between dies to begin the process of reducing the space between the powder particles. The compacted powder product is then heated to a high temperature to produce a solid component.
Sintering is the general term used to describe a process in which a powder is compacted into a solid using heat and/ or pressure.
The process of sintering is used with a wide variety of materials, especially those with properties that prevent shaping by melting and casting.
The starting powder is mixed with a lubricant/binder and is then moulded to shape by compressing it in a die. The compacted part is then sintered by heating at a high temperature, sometimes under pressure, for a prolonged period of time. Very high temperatures and/or pressure are used during sintering to minimise porosity.
In powder processing, the volume of the workpiece does not stay constant. As the powder fuses together, most of the spaces between the powder particles disappear and the volume of the finished component is considerably reduced.
Sintering is sometimes economically competitive with alternative methods of shaping. A wide variety of components can be manufactured using powder processing such as domestic ceramics for applications such as a bathroom sink.
T193, Forming, Rolling, Forging, Extrusion, Wire drawing, Powder processing, Sheet forming
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|