Nuclear Radiation
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-06-08
Topic: 120 see comments
Post views: 1035
Nuclear Radiation
Overview
The nuclei of all the isotopes of elements heavier than lead (which has 82 protons and 125 neutrons) are unstable, or radioactive.
This means that they spontaneously emit high-energy atomic particles or radiation in a process known as radioactive decay.
As a consequence, they may become nuclei of different elements or isotopes of the same element.
Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MGj_aJz7cTs&list=PLZWd11MQ093F3UQ0X3cKIjrBszT-N9oHh&index=5
Radioactive Decay
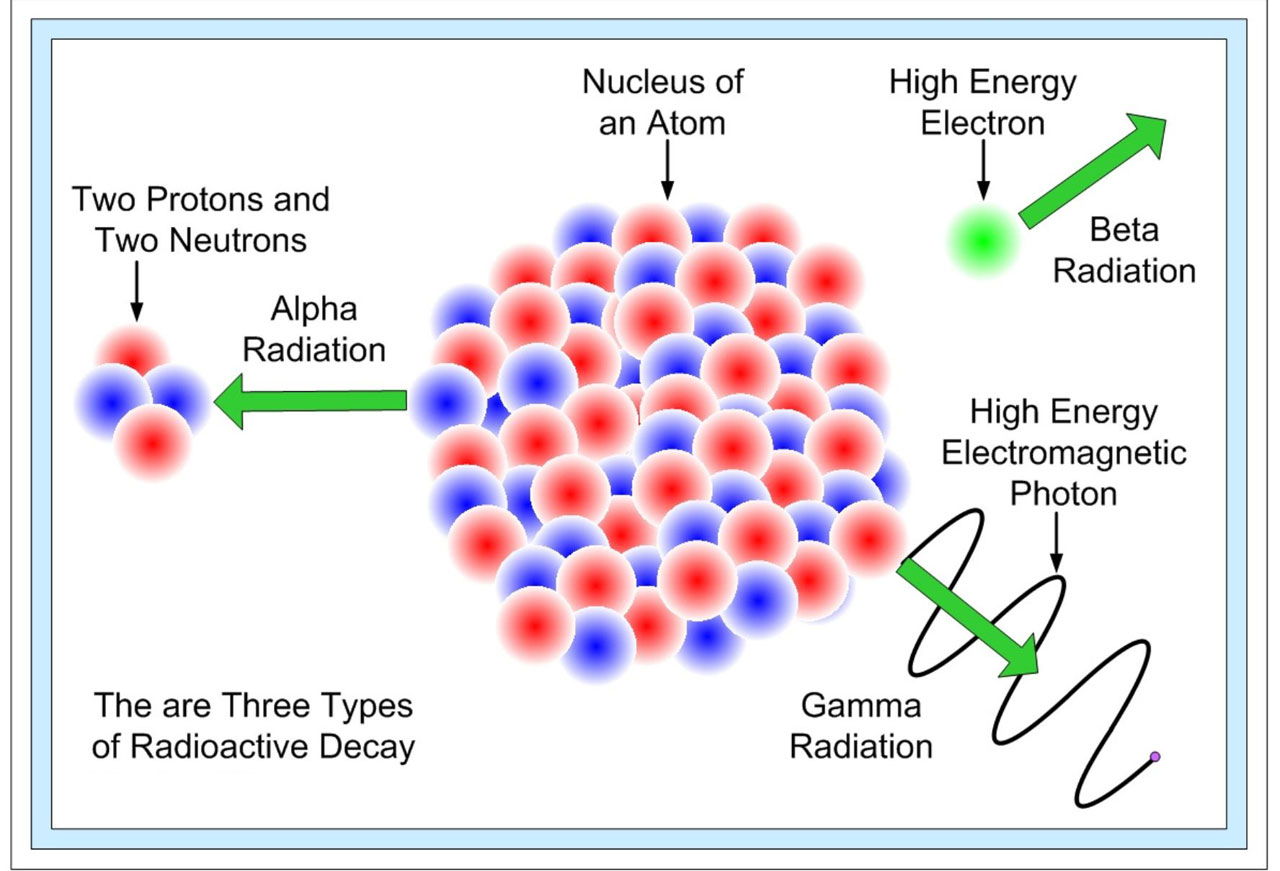
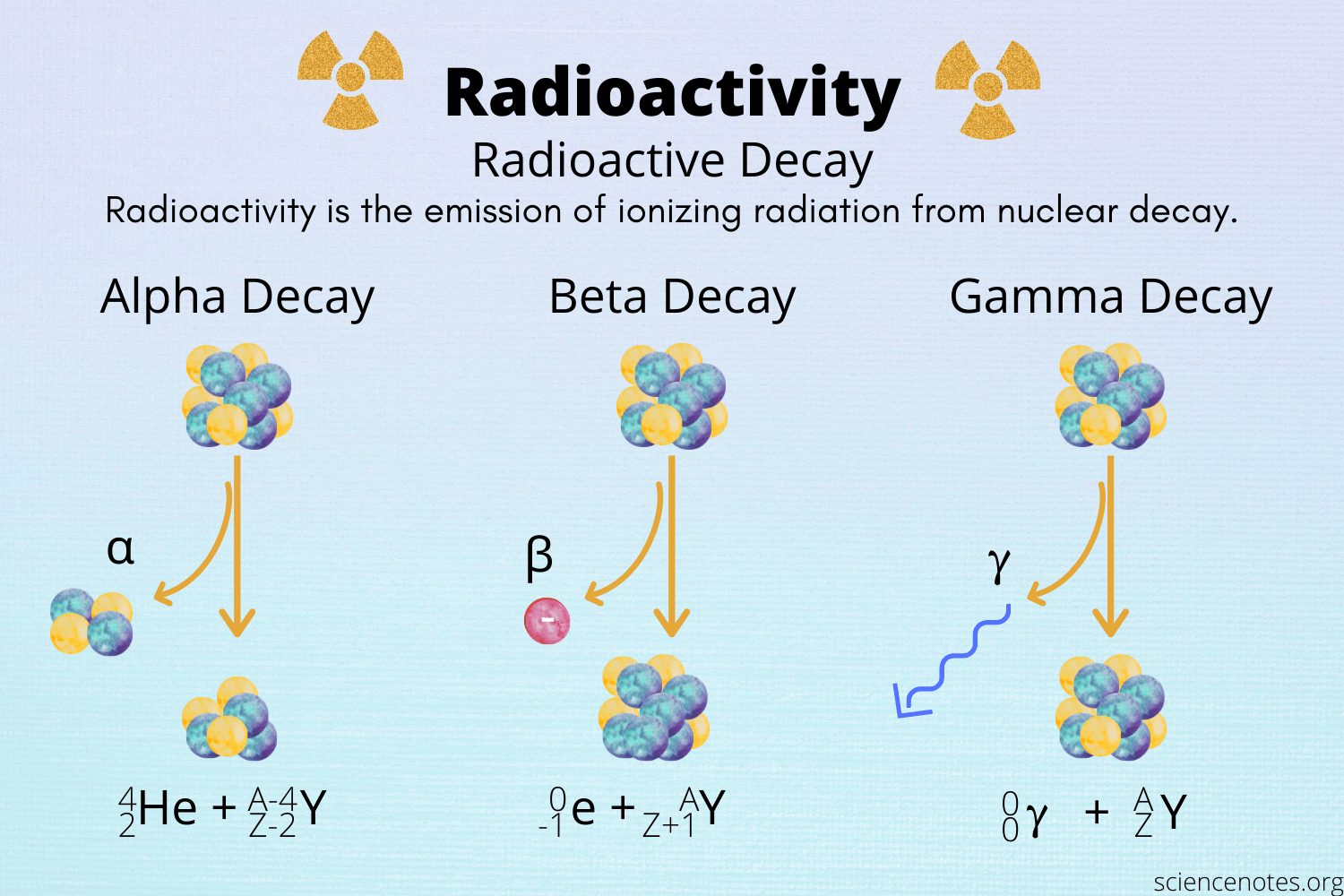
Three types of particle can be emitted during radioactive decay.
Alpha Particles (α-particles) these particles have relatively low energy and can be stopped by a sheet of paper, a few cm of air or human skin. They can cause serious human health problems if a source is inhaled or ingested from contaminated food.
Beta Particles (β-particles) consists of electrons released from neutron decay. They have a higher energy and are more penetrating than α-particles, but can still be stopped by a few mm of metal. Exposure to β-particles can cause burns to the skin, but for serious harm to occur, the source must be ingested or inhaled.
Gamma Radiation (γ-radiation) a form of electromagnetic radiation with a short wavelength. Like light, gamma radiation can be treated either as waves or as particles (photons). It is release when a nucleus releases surplus energy usually from one of the other forms of nuclear decay. Gamma particles are stopped only by several cm of lead or steel, or a few feet of concrete; together with neutrons, they are the chief radiation hazard associated with nuclear technology.
Fission
Nuclear fission is the process that takes place when a heavier atom splits into two lighter atoms, with the release of subatomic particles (such as electrons and neutrons) and energy in the form of radiation and heat.
When the nucleus of an atom of uranium 235 (235U) is hit by a neutron, this neutron can be absorbed into the nucleus. The probability of absorption depends heavily on the energy, or speed, of the neutron. The resulting larger nucleus is unstable. The atom divides into two smaller atoms, krypton (Kr) and barium (Ba), and releases a large amount of energy and three further neutrons, along with β-particles and γ-radiation.
The new neutrons produced have a chance of going on to hit another atom of 235U and potentially be absorbed causing it to break down in turn, creating a chain reaction.
The amount of absorption by atoms that do not undergo fission can be controlled by the use of control rods which contain neutron-absorbing materials such as boron.
1 gram of 235U releases about 8 × 1010 J. This compares with the release of about 2.5 × 104 J when the same mass of coal is burned.
Half-Life
The half-life of a radioactive element is defined as the amount of time it takes for a given mass of the element to decay to 50% of its original mass (much of this ‘lost mass’ is converted into the decay products).
The half life can also be though of as the amount of time it takes for the radiation released to fall by half.
Units for Measuring Radiation
Radiaoactivity is measured in becquerels (Bq). 1 Bq represents a rate of decay of one nucleus per second.
A normal adult releases around 5000 Bq due to the presence of naturally ocurring potassium in the body. Radioactivity releases are often expressed in terms of petabecquerels (PBq), where 1 PBq is equal to 1015 Bq.
Releases of radiation can also be weighted to allow for their severity when humans are exposed to them. This weighting takes account of the type of radiation (for instance, neutrons and alpha particles are more damaging than X-rays and gamma rays). Weighted doses are measured in sieverts (Sv) or millisieverts (mSv). The sievert is based on the radiation dose absorbed by the recipient multiplied by a 'quality factor'. For example, radiation from alpha particles has a quality factor 20 times that of the same quantity of radiation from X-rays.
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|