Derivatives (Calculus)
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-08-01
Topic: 152 see comments
Post views: 1186
Derivatives
Tangent
The tangent to a curved graph at a particular point is the straight line that ‘just touches’ it. The gradient of the graph at that point is the gradient of the tangent.
Differentiable
A function ‘f’ is differentiable at a particular value of ‘x’ if its graph has a gradient at the point (x, f (x)).
Derivative (or derived function)
The derivative is the slope of the line tangent to the curve at a particular point.
OU Explanation:
“The derivative (or derived function) of a function ‘f’ is the function f ‘ (f prime) such that f ‘ (x) is equal to the gradient of the graph of ’f’ at the point (x, f (x))”
Domain
The domain of f ‘ consists of all the values in the domain of ‘f’ at which ‘f’ is differentiable.
Lagrange & Leibniz notation
In Lagrange notation, the derivative of a function ‘f’ is denoted by f '.
In leibniz notation, if y = f (x), then f ' (x) is denoted by (dy / dx) or (d / dx)(f (x))
The quantity (dy / dx) is called the derivative of y with respect to x.
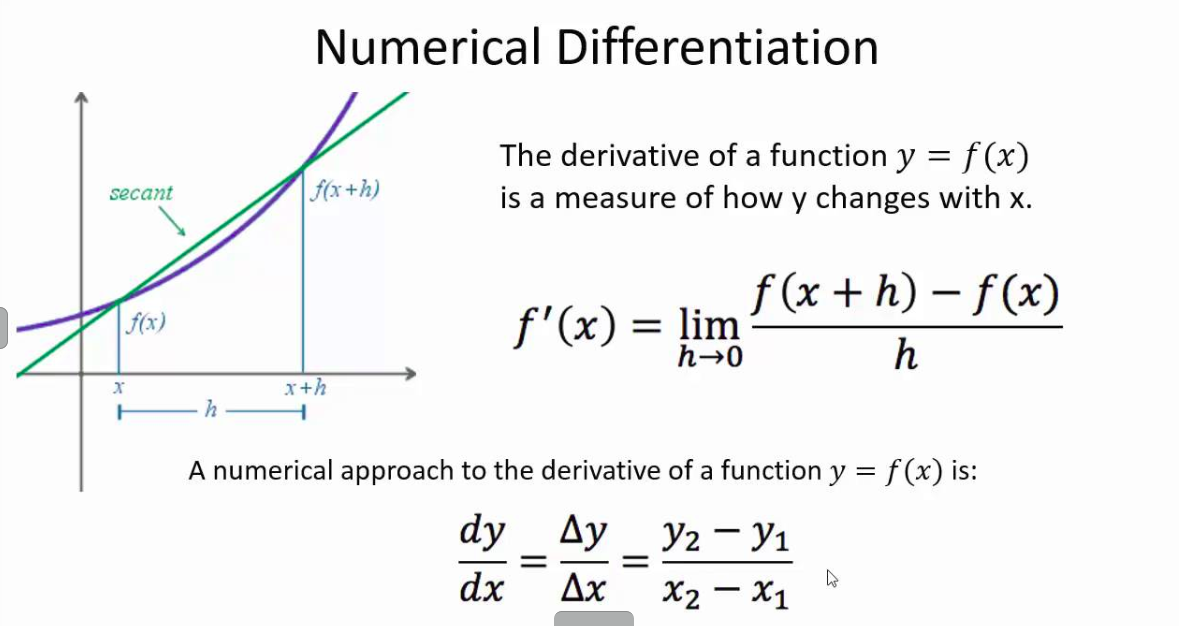
Differentiation from first principles
The basic method of differentiation from first principles is as follows:
For a function x(t), we can find an expression for dx/dt by following these steps;
- Find an expression for 𝛿x:
- Write an expression for x at point t
- Write an expression for x + 𝛿x at point t + 𝛿t
- Subtract the first expression from the second.
- Find 𝛿x/𝛿t by dividing both sides of your equation for 𝛿x by 𝛿t
- Take the limit of 𝛿x/𝛿t as 𝛿t approaches zero to obtain an expression for 𝛿x/𝛿t. Expressing this as an equation, we have:
dx/dt = lim/𝛿t⇢0 [ x(t + 𝛿t) − x (t) ] / [ 𝛿t ]
Where the notation lim/𝛿t⇢0 means ‘the limit as h goes towards zero of’ (the value approached as h approaches zero).
Difference quotient
The difference quotient for ‘f’ at ‘x’ is the fraction in the equation above. It is the gradient of the line through the points (x, f (x)) and (x + h, f (x + h))
Derivatives of a power function
A power function is a function of the form f (x) = xn, where n is a real number.
The power function f (x) = xn has derivative:
f ' (x) = nxn-1
you could also write this using Leibniz notation as:
(d / dx)(xn) = nxn-1
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|