Solar Panels
By DarthVader
Date: 2022-06-14
Topic: 130 see comments
Post views: 1161
Solar Panels
Maximum Current
At 100% efficiency, the current produced by a PV cell per unit area would equal the charge of each electron (in C) multiplied by the photon flux (in photons per second per m-2):
Electron charge = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Typical photon flux = 3 × 1021 s-1 m-2
So the theoretical current that can be produced per sqaure metre is:
(1.6 × 10-19 C) × (3 × 1021 s-1 m-2) = 480 C s-1 m-2
= 480 A m-2
In practise, 100% efficiency not currently possible. A more realistic estimate would be around 50% efficiency which would give:
240 A m-2
Maximum voltage
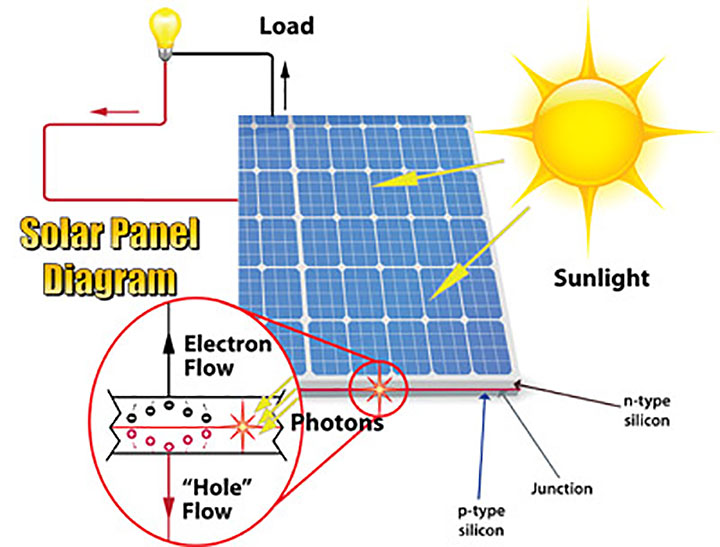
The voltage generated by a solar cell is proportional to the amount of available light.
The maximum voltage is governed by the energy threshold of the material used.
The maximum voltage expressed in volts, is numerically equal to the threshold energy expressed in electron volts (eV).
For silicon (Si), the threshold energy is 1.1 eV, so the ‘maximum’ possible voltage of a silicon cell is 1.1 V
In practise, the maximum voltage produced by a typical PV cell will be around 50% of this as it would require a very high intensity of illumination to produce the full 1.1 V.
So typically a well performing PV cell will produce around 0.6 V
Maximum power output
To calculate power output:
solar energy (W m-2) × cell area (m2) × cell efficiency = power output (W)
The power output of a solar cell depends on 3 things:
- The material of the cell
- The cell area
- The amount of sunlight falling on it
A typical silicon cell in full sunlight (AM1.5, 1000 W m-2), produces a current of about 240 A m-2 at a voltage of around 0.6 V.
From P = IV, we can calculate the power in watts:
240 A m-2 × 0.6 V = 144 W m-2
This represents about 14% efficiency from the 1000 W m-2 of average solar irradience.
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|