Battery Cells
By DarthVader
Date: 2023-04-16
Topic: 196 see comments
Post views: 832
Battery Cells
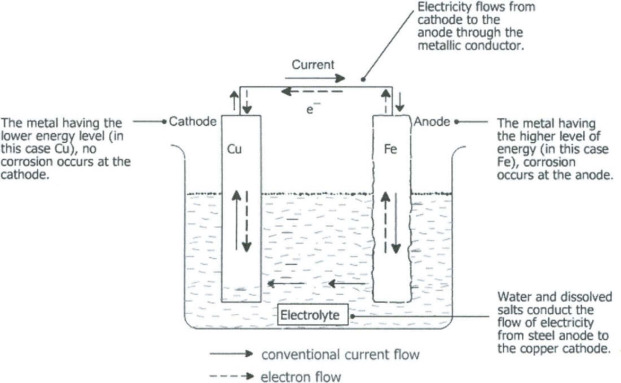
A battery cell works by connecting two conducting electrodes via an electrolytic solution.
1. Components of a Battery Cell
A typical battery cell consists of three main components:
- Anode (Negative Electrode): Typically made of a material like lithium, zinc, or graphite. This is where oxidation (loss of electrons) happens.
- Cathode (Positive Electrode): Made of a material like a metal oxide (e.g., lithium cobalt oxide). This is where reduction (gain of electrons) happens.
- Electrolyte: A medium that allows ions to flow between the anode and cathode. It can be a liquid, gel, or solid.
2. How It Generates Electricity
Electricity is generated when the battery is connected to an external circuit, allowing electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode.
Discharge Process (Battery in Use)
Oxidation at the Anode: When the battery is in use, a chemical reaction occurs at the anode, causing it to release electrons. These electrons travel through the external circuit, powering devices (such as a light bulb, phone, etc.).
- For example, in a lithium-ion battery, lithium atoms in the anode lose electrons and become lithium ions (Li⁺).
Ion Flow Through the Electrolyte: At the same time, positively charged ions (Li⁺ in the case of lithium-ion batteries) move through the electrolyte toward the cathode.
Reduction at the Cathode: At the cathode, a reduction reaction takes place, where the electrons that traveled through the external circuit combine with ions (e.g., Li⁺) that traveled through the electrolyte. This completes the chemical reaction at the cathode.
Example (Lithium-Ion Battery)
In a lithium-ion battery:
- Anode (Negative): Lithium atoms release electrons and form Li⁺ ions.
- Cathode (Positive): Li⁺ ions move through the electrolyte to the cathode and combine with electrons to form lithium atoms, storing energy.
3. Recharging (for Rechargeable Batteries)
In rechargeable batteries, the process can be reversed by applying an external electrical current. This drives the electrons from the cathode back to the anode, restoring the battery to its original state.
- Recharging: The external power source forces electrons back into the anode, and the ions move from the cathode to the anode, preparing the battery for another cycle of use.
4. Energy Storage
During discharge, chemical energy is released as electrical energy. In rechargeable batteries, energy is stored chemically during charging.
Key Takeaways:
- Electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit, generating electricity.
- Ions flow inside the battery through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode during discharge.
- In rechargeable batteries, this process is reversed during charging.
This electrochemical cycle enables batteries to power devices and store energy efficiently.
| Comments | Creator | Date | ID |
|---|